Human-AI tools for Accounting for Differences Across Contexts
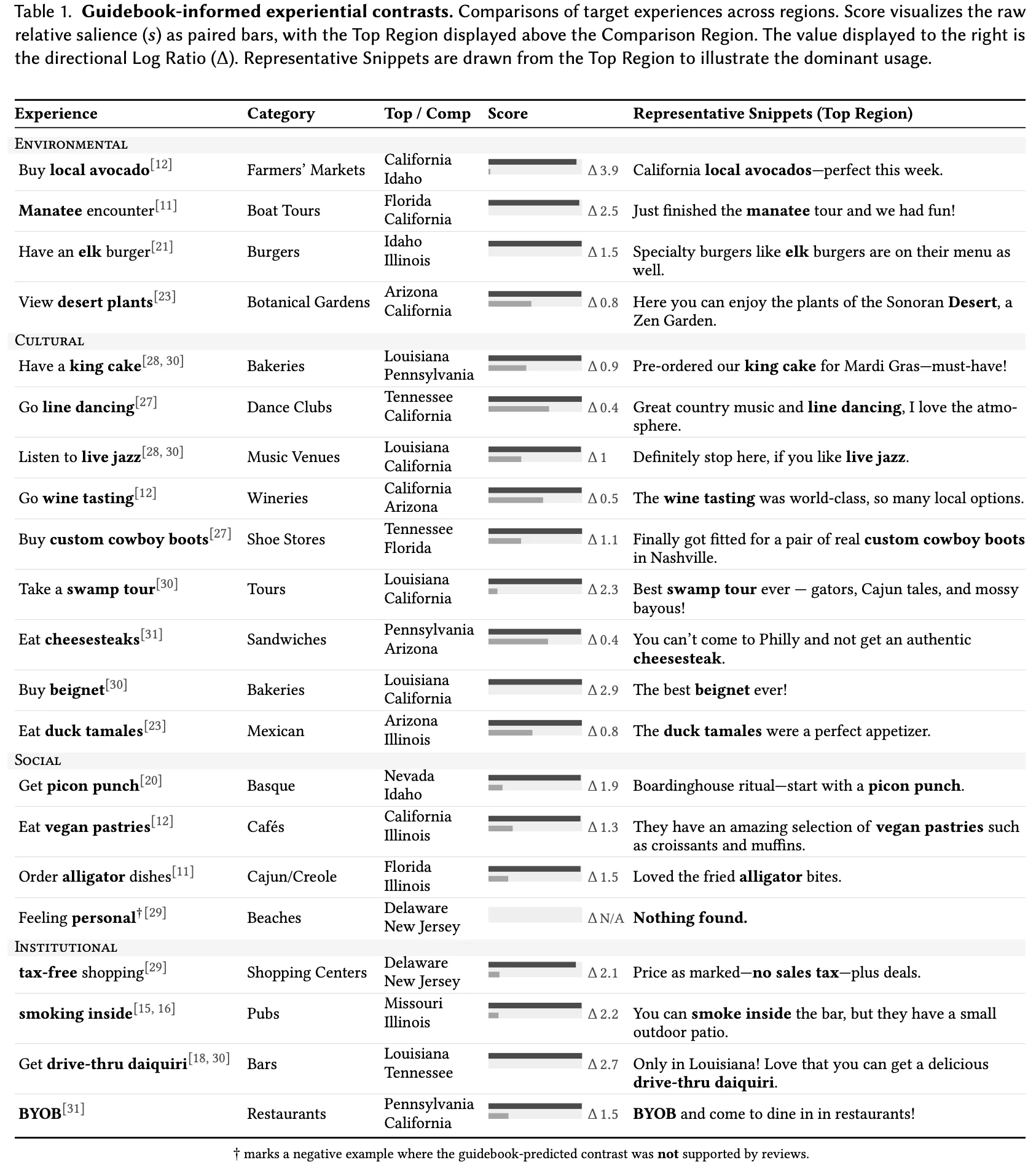
Project description
How do cultural, social, and geographical contexts shape the way people engage with activities and concepts? Our system provides an interactive, data-driven approach to exploring these contextual differences across locations.
Built on large-scale textual data from sources like Yelp, the system enables users to compare how specific activities or concepts vary between regions. Unlike traditional methods that rely on simple frequency-based metrics, our approach leverages BM25, a ranking algorithm that effectively handles document length variations and category granularity issues. To enhance interpretability, we introduce a threshold-based relevance framework, dynamically categorizing differences into engagement, relevance, and significance levels based on score distributions.
Users can input a query (e.g., "sunbathing" in Florida vs. Pennsylvania) and receive visually intuitive comparisons that highlight key contextual variations. The system’s interactive charts make complex data easily interpretable, providing insights for researchers, businesses, and individuals seeking a deeper understanding of regional differences in human behavior and activity patterns.
This project contributes to the broader field of human-computer interaction and computational social science, demonstrating how AI can assist in interpreting and visualizing nuanced contextual shifts. Future developments will focus on expanding data sources, improving semantic understanding, and enabling real-time adaptability to make comparisons even more precise and insightful.
Figures
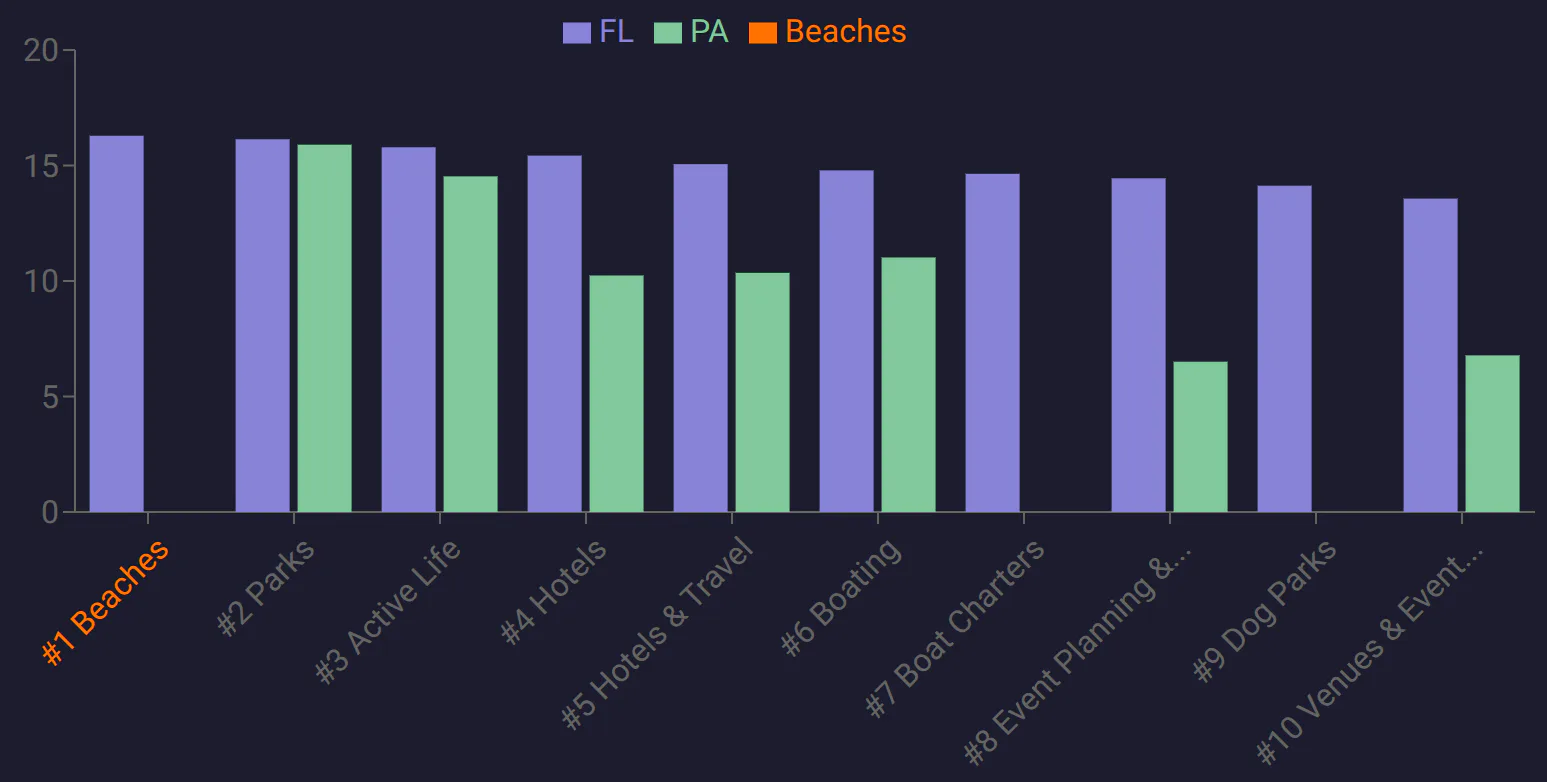
Figure 1: Bar chart visualization for "sunbathing" from FL to PA at beaches.
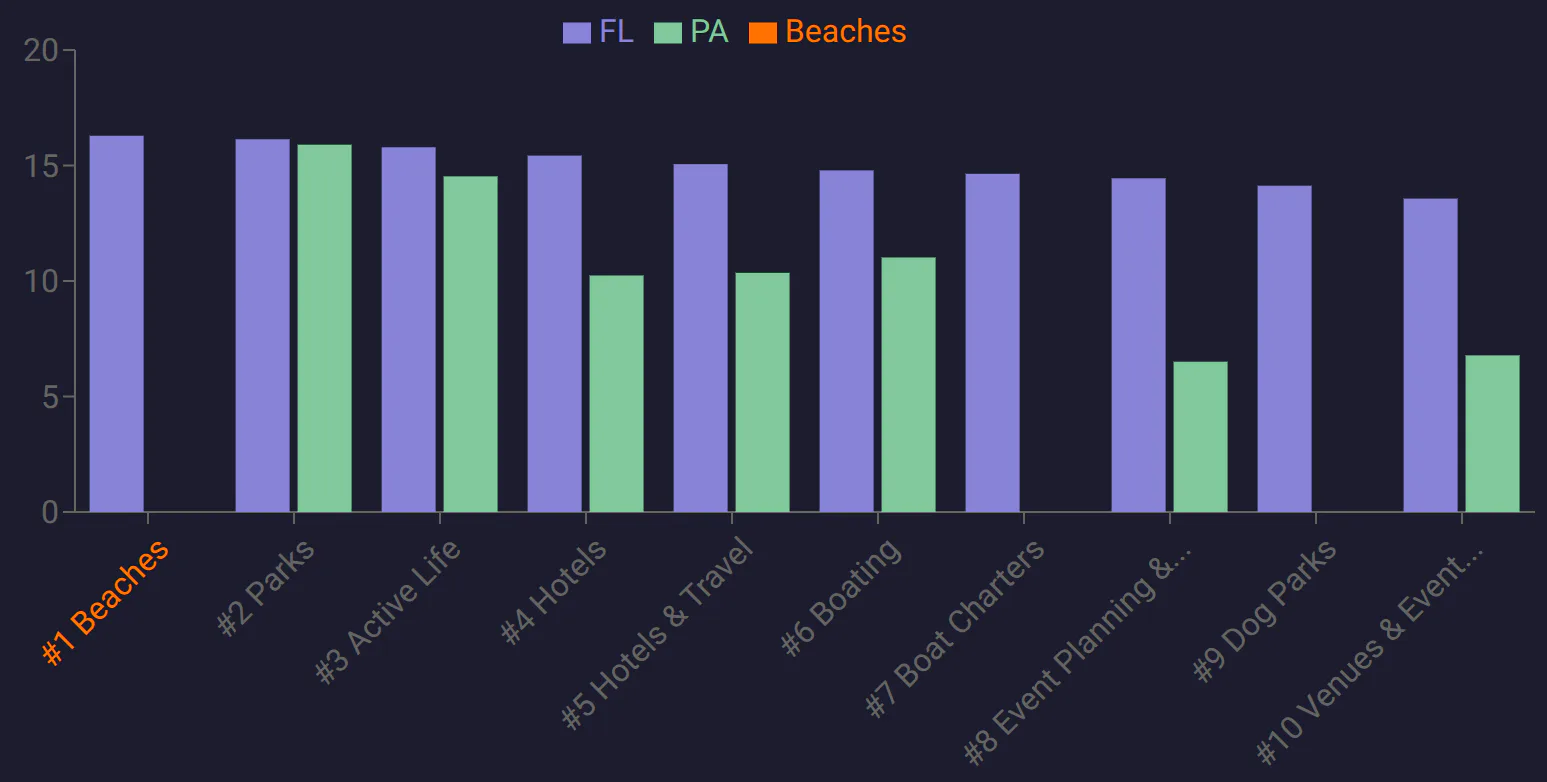
Figure 2: Line chart visualization for "sunbathing" from FL to PA at beaches.
Publications
- A Human-Centered Classifier for Cross-Setting DifferencesDTR Deliverable - Spring 2023
View paper
- Accounting for Differences: AI’s Role in Contextual and Cultural Analysis to a Concept ExpressionDTR Deliverable - Fall 2023
View paper
- Adapting to Diversity: Enhancing Context-Aware AI Through Regional Sensitivity and Automated AnalysisDTR Deliverable - Winter 2024
View paper
- Human-AI Tools for Contextualizing Differences: Bridging Data-Driven Insights with Real-World InterpretabilityDTR Deliverable - Winter 2025
View paper
Team
Faculty
- Haoqi Zhang
Masters and Undergraduate Students
- Medini Chopra
- Zhuoran (Elara) Liu
- Alumni: Jiayi Zheng
- Alumni: Suhuai Chen
- Alumni: Yiran Mo